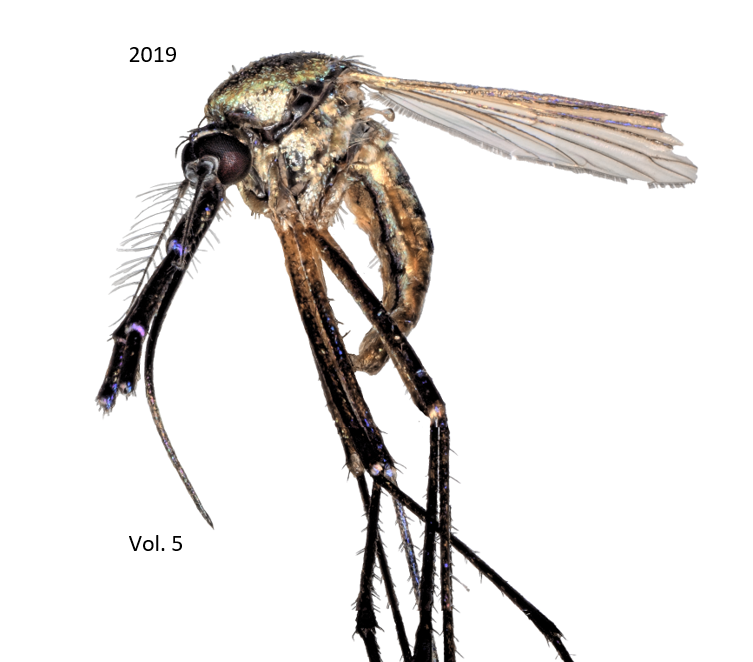
Level of Insecticide Control in Pseudomyrmex brunneus Using Raid
Abstract
Ants have been considered major household pests for some time, leading to the introduction of several different insecticides to protect against them. These insecticides have proven to be harmful to mammals in multiple metabolic functions. In this experiment, the ant species Pseudomyrmex brunneus, of the order Hymenoptera and the family Formicidae, was used as a test subject to show the effectiveness of different insecticides. The three different insecticides tested were Raid, Spectracide, and a home remedy. The first experiment performed had many methodological flaws that resulted from not using a correct time frame for recording ant death and improper use of Spectracide. Due to these experimental errors, a second experiment was performed in which dilutions of Raid with water were used to test which would be most effective in killing the ants. This resulted in the 1:1 dilution being most effective and the 1:3 dilution being least effective in regards to time of death, but all three dilutions did result in 100% ant death in less than six minutes. This result is important because it shows that dilutions of a common household insecticide can be used to kill the same number of ants and could possibly be safer for those who are exposed to the insecticide in the home.References
Achudume, A. C., Nwoha, P. U. and Ibe, J. N. 2010. Effects of dietary exposure to
insecticide Raid® on the survival, growth and inhibition of metabolic processes in Wistar
rats."Journal of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology 2.8:
-125.
Achudume, A. C., Nwoha, P. C. and Ibe, J. N. 2009. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of the
insecticide "Raid† in Wistar rats. J. Environ. Toxicol., 24: 357—361
Bradberry, S.M., Cage, S.A., Proudfoot, A. T., Vale, J. A. 2005. Poisoning due to pyrethroids.
J. Toxicol. Rev. 24: 93.
Drees, B. 2012. Collecting and Maintaining Colonies of Red Imported Fire Ants for Study.
(USDA) U.S. Department of Agriculture ENTO-028.
Laskowski, D.A. 2002. Physical and chemical properties of pyrethroids. Rev. Environ. Contam.
Toxicol. 174:49-170
Martin, M., Rodriguez, K., Sanchez-Sauco, M., Zambudio-Carmona, G., Ortega-Garcia,
J.A. 2009. Household exposure to pesticides and bladder exstrophy in a newborn baby
boy: a case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Reports 3:6626
Prakash, M. 2017. A common class of insecticides puts farmers at high risk of diabetes.
http://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/toxic-spray-57309
Shafer, T. J., Meyer, D. A., & Crofton, K. M. 2005. Developmental neurotoxicity of pyrethroid insecticides: Critical review and future research needs. Environmental Health
Perspectives 113(2):123—136
Ward, P.S. 1989. Systematic studies on pseudomyrmecine ants: revision of the Pseudomyrmex
oculatus and P. subtilissimus species groups, with taxonomic comments on other species.
Quaest. Entomol. 25:393-468.
Ward, P. S. 1985. The Nearctic species of the genus Pseudomyrmex (Hymenoptera:
Formicidae). Quaest. Entomol. 21: 209-246
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Instars supports the need for authors to share, disseminate and maximise the impact of their research. We take our responsibility as stewards of the online record seriously, and work to ensure our policies and procedures help to protect the integrity of scholarly works.
License to the Journal. The Author hereby licenses to the Journal the irrevocable, nonexclusive, and royalty-free rights as follows:
a. The Journal may publish the Article in any format, including electronic and print media. Specifically, this license include the right to reproduce, publicly distribute and display, and transmit the Article or portions thereof in any manner, through any medium now in existence or developed in the future, including but not limited to print, electronic, and digital media, computerized retrieval systems, and other formats
b. The Journal may prepare translations and abstracts and other similar adaptations of the Article in furtherance of its publication of the Article.
c. The Journal may use the Author's name, likeness, and institutional affiliation in connection with any use of the Article and in promoting the Article or the Journal.
d. The Journal may exercise these rights directly or by means of third parties. The Journal may authorize third-party publishers, aggregators, and printers to publish the Article or to include the Article in databases or other services. [Examples of such third parties include Westlaw, Lexis, and EBSCO.]
e. The Journal may without further permission from the Author transfer, assign, or sublicense the rights that the Journal has pursuant to the Agreement.
f. In order to foster wider access to the Article, especially for the benefit of the nonprofit community, the Author hereby grants to the Journal the authority to publish the Article with a Creative Commons "Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives" license. [The Author should consult the Creative Commons website (www.creativecommons.org) for further information]
g. This liscense of rights to the Journal shall take effect immediately. In the event that the Journal does not publish the Article, this license to the Journal shall temrinate upon written notification by the Journal to the Author, or upon termination of all publication by the Journal. To the extent that moral rights may apply to the Article, this agreement does not affect the moral rights of the Author in or to the Article.
Rights of the Author. Without suggesting any limit on other rights that the Author may h ave with respect to the Article, the Author retains the following rights. To the extent that the Journal holds similar rights with respect to the Article consistent with this Agreement, the Author shall hold these rights on a nonexclusive basis. To the extent that the Article includes edits and other contributions by the staff of the Journal, the rights of the Author in this Paragraph include the right to use such edits and contributions.
a. The Author may publish the Article in another scholarly journal, in a book, or by other means. The Author may exercise this right of publication only after the date of first publication of the ARticle in the Journal in any format.
b. The Author shall, without limitation, have the right to use the ARticle in any form or format in connection with the Author's teaching, conference presentations, lectures, other scholarly works, and for all of Author's academic and professional acitvities.
c. The Author shall at any time have the fright to make, or to authorize others to make, a preprint or a final published version of the ARticle available in digital form over the Internet, including, but not limited to, a website under the control fo the Author or the Author's employer or through digital repositories including, but not limited to, those maintained by scholarly societies, funding agencies, or the Author's employer. This right shall include, without limitation, the right of the Author to permit public access to the Article as part of a repository or through a service or domain maintained by teh Author's employing the institution or a service as required by law or by agreement with a funding agency. The Journal may in its discretion deposit the ARticle with any digital repository consisten with deposits permitted by the Author under ths paragraph. [Examples of such repositories include SSRN, arXiv.org, PubMed Central, and Academic Commons at Columbia University.]
d. Any of the foregoing permitted uses of the Article, or of a work based substantially on the Article, shall include an appropriate citation to the Article, stating that it has been or is to be published in the Journal, with name and date of the Journal publication and the Internet address for the website of the Journal.
Editing of the Article. This Agreement is subject to the understanding that the ordinary editing processes of the Journal will be diligently pursued and that the Article will not be published by the Journal unless, in tis final form, it is acceptable to the Author and the Journal.